Use parameters in Azure Monitor dashboards
Parameters are used as building blocks for dashboard filters in Azure Monitor dashboards. They're managed in the dashboard scope, and can be added to queries to filter the data presented by the underlying visual. A query can use one or more parameters. This document describes the creation and use of parameters and linked filters in Azure Monitor dashboards.
[!NOTE] Parameter management is available in edit mode to dashboard editors.
View parameters list
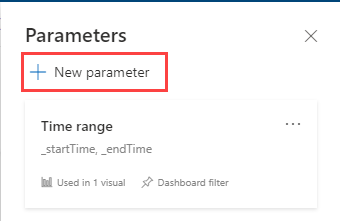
Select the Parameters button at the top of the dashboard to view the list of all dashboard parameters.
![]()
Create a parameter
To create a parameter, select the New parameter button at the top of the right pane.
Properties
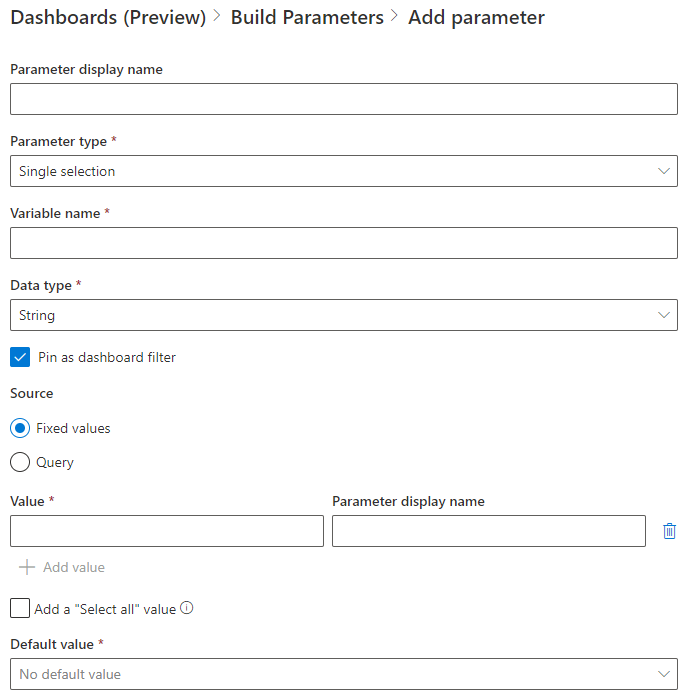
- In the Add parameter pane, configure the properties detailed below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Parameter display name | The name of the parameter shown on the dashboard or the edit card. |
| Parameter type | One of the following parameters:
|
| Variable name | The name of the parameter to be used in the query. |
| Data type | The data type of the parameter values. |
| Pin as dashboard filter | Pin the parameter-based filter to the dashboard or unpin from the dashboard. |
| Source | The source of the parameter values:
|
| Add a “Select all” value | Applicable only to single selection and multiple selection parameter types. Used to retrieve data for all the parameter values. This value should be built into the query to provide the functionality. See Use the multiple-selection query-based parameter for more examples on building such queries. |
Manage parameters in parameter card
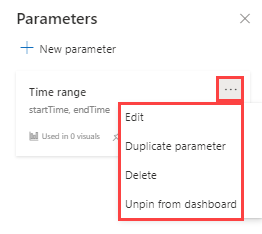
In the three dots menu in the parameter card, select Edit, Duplicate parameter, Delete, or Unpin from dashboard/Pin to dashboard.
The following indicators can be viewed in the parameter card:
- Parameter display name
- Variable names
- Number of queries in which the parameter was used
- Pin/unpin state in the dashboard
Use parameters in your query
A parameter must be used in the query to make the filter applicable for that query visual. Once defined, you can see the parameters in the Query page > filter top bar and in the query intellisense.
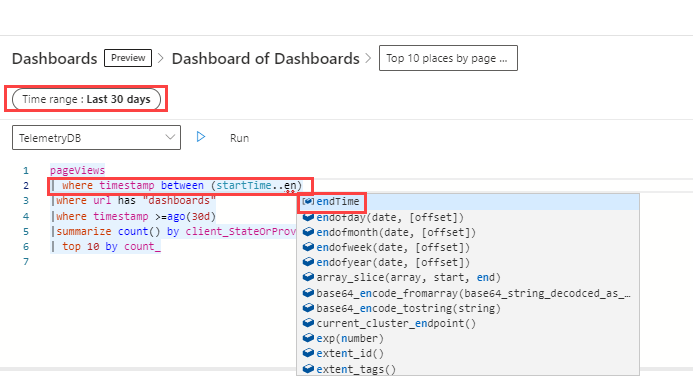
[!NOTE] If the parameter isn't used in the query, the filter remains disabled. Once the parameter is added to the query, the filter becomes active.
Use different parameter types
Several dashboard parameter types are supported. The following examples describe how to use parameters in a query for various parameter types.
Use the default Time range parameter
Every dashboard has a Time range parameter by default. It shows up on the dashboard as a filter only when used in a query. Use the parameter keywords _startTime and __endTime to use the default time range parameter in a query as seen in the following example:
>EventsAll
| where Repo.name has 'Microsoft'
| where CreatedAt between (_startTime.._endTime)
| summarize TotalEvents = count() by RepoName=tostring(Repo.name)
| top 5 by TotalEvents
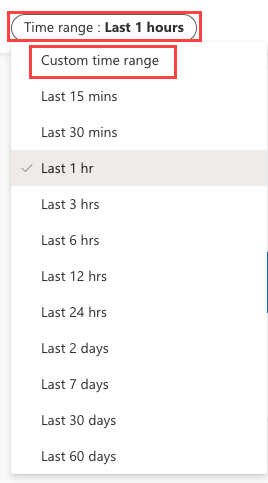
Once saved, the time range filter shows up on the dashboard. Now it can be used to filter the data on the card. You can filter your dashboard by selecting from the drop-down: Time range (last x minutes/hours/days) or a Custom time range.
Use the single selection fixed value parameter
Fixed value parameters are based on predefined values specified by the user. The following example shows you how to create a single selection fixed value parameter.
Create the parameter
-
Select Parameters to open the Parameters pane and select New parameter.
-
Fill in the details as follows:
- Parameter display name: Company
- Parameter type: Single selection
- Variable name:
_company - Data type: String
- Pin as dashboard filter: checked
- Source: Fixed values
In this example, use the following values:
Value Parameter display name google/ Google microsoft/ Microsoft facebook/ Facebook aws/ AWS uber/ Uber - Add a Select all value: Unchecked
- Default value: Microsoft
-
Select Done to create the parameter.
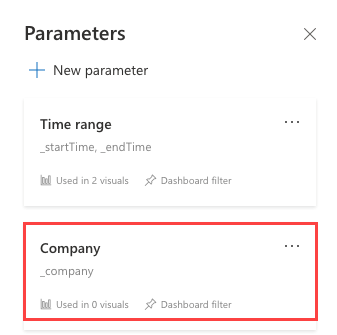
The parameters can be seen in the Parameters side pane, but aren't currently being used in any visuals.
Use the parameter
-
Run a sample query using the new Company parameter by using the
_companyvariable name:>EventsAll | where CreatedAt > ago(7d) | where Type == "WatchEvent" | where Repo.name has _company | summarize WatchEvents=count() by RepoName = tolower(tostring(Repo.name)) | top 5 by WatchEventsThe new parameter shows up in the parameter list at the top of the dashboard.
-
Select different values to update the visuals.

Use the multiple-selection fixed-value parameters
Fixed value parameters are based on predefined values specified by the user. The following example shows you how to create and use a multiple-selection fixed-value parameter.
Create the parameters
-
Select Parameters to open the Parameters pane and select New parameter.
-
Fill in the details as mentioned in Use the single selection fixed value parameter with the following changes:
- Parameter display name: Companies
- Parameter type: Multiple selection
- Variable name:
_companies
-
Click Done to create the parameter.
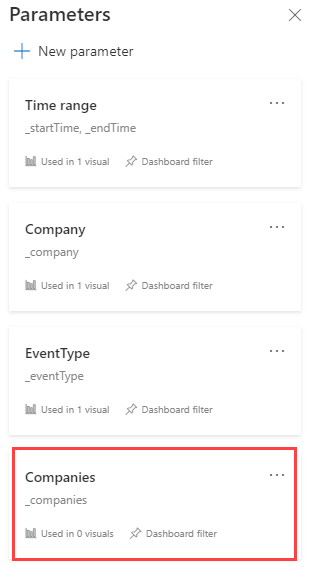
The new parameters can be seen in the Parameters side pane, but aren't currently being used in any visuals.
Use the parameters
-
Run a sample query using the new companies parameter by using the
_companiesvariable.>EventsAll | where CreatedAt > ago(7d) | extend RepoName = tostring(Repo.name) | where Type == "WatchEvent" | where RepoName has_any (_companies) | summarize WatchEvents=count() by RepoName | top 5 by WatchEventsThe new parameter shows up in the parameter list at the top of the dashboard.
-
Select one or more different values to update the visuals.

Use the single selection query-based parameter
Query-based parameter values are retrieved during dashboard loading by executing the parameter query. The following example shows you how to create and use a single selection query-based parameter.
Create the parameter
-
Select Parameters to open the Parameters pane and select New parameter.
-
Fill in the details as mentioned in Use the single selection fixed value parameter with the following changes:
- Parameter display name: Event
- Variable name:
_event - Source: Query
- Data source: GitHub
- Select Add query and enter the following query. Select Done.
>EventsAll | distinct Type | order by Type asc- Value: Type
- Display name: Type
- Default value: WatchEvent
-
Select Done to create the parameter.
Use a parameter in the query
-
The following sample query with the new Event parameter uses the
_ eventvariable:>EventsAll | where Type has (_event) | summarize count(Id) by Type, bin(CreatedAt,7d)The new parameter shows up in the parameter list at the top of the dashboard.
-
Select different values to update the visuals.
Use the multiple-selection query-based parameter
Query-based parameter values are derived at dashboard load time by executing the user specified query. The following example shows how to can create a multiple-selection query-based parameter:
Create a parameter
-
Select Parameters to open the Parameters pane and select New parameter.
-
Fill in the details as mentioned in Use the single selection fixed value parameter with the following changes:
- Parameter display name: Events
- Parameter type: Multiple selection
- Variable name:
_events
-
Click Done to create the parameter.
Use parameters in the query
-
The following sample query uses the new Events parameter by using the
_eventsvariable.>EventsAll | where Type in (_event) or isempty(_events) | summarize count(Id) by Type, bin(CreatedAt,7d)[!NOTE] This sample uses the Select All option by checking for empty values with the
isempty()function.The new parameter shows up in the parameter list at the top of the dashboard.
-
Select one or more different values to update the visuals.
Use the free text parameter
Free text parameters don't contain any values. They allow you to introduce your own value.
Create the parameter
- Select Parameters to open the Parameters pane and select New parameter.
- Fill in the details as follows:
- Parameter display name: Company
- Parameter type: Free text
- Variable name: _company
- Data type: String
- Pin as dashboard filter: checked
- Default value: No default value
Use parameters in the query
-
Run a sample query using the new Company parameter by using the
_companyvariable name:>EventsAll | where CreatedAt > ago(7d) | where Type == "WatchEvent" | where Repo.name has _company | summarize WatchEvents=count() by RepoName = tolower(tostring(Repo.name)) | top 5 by WatchEvents
The new parameter is now visible in the parameter list at the top of the dashboard.
Use filter search for single and multiple selection filters
In single and multiple selection filters, type the value that you want. The filter search will present only the recently retrieved values that match the search term.